Rad Man Minerals
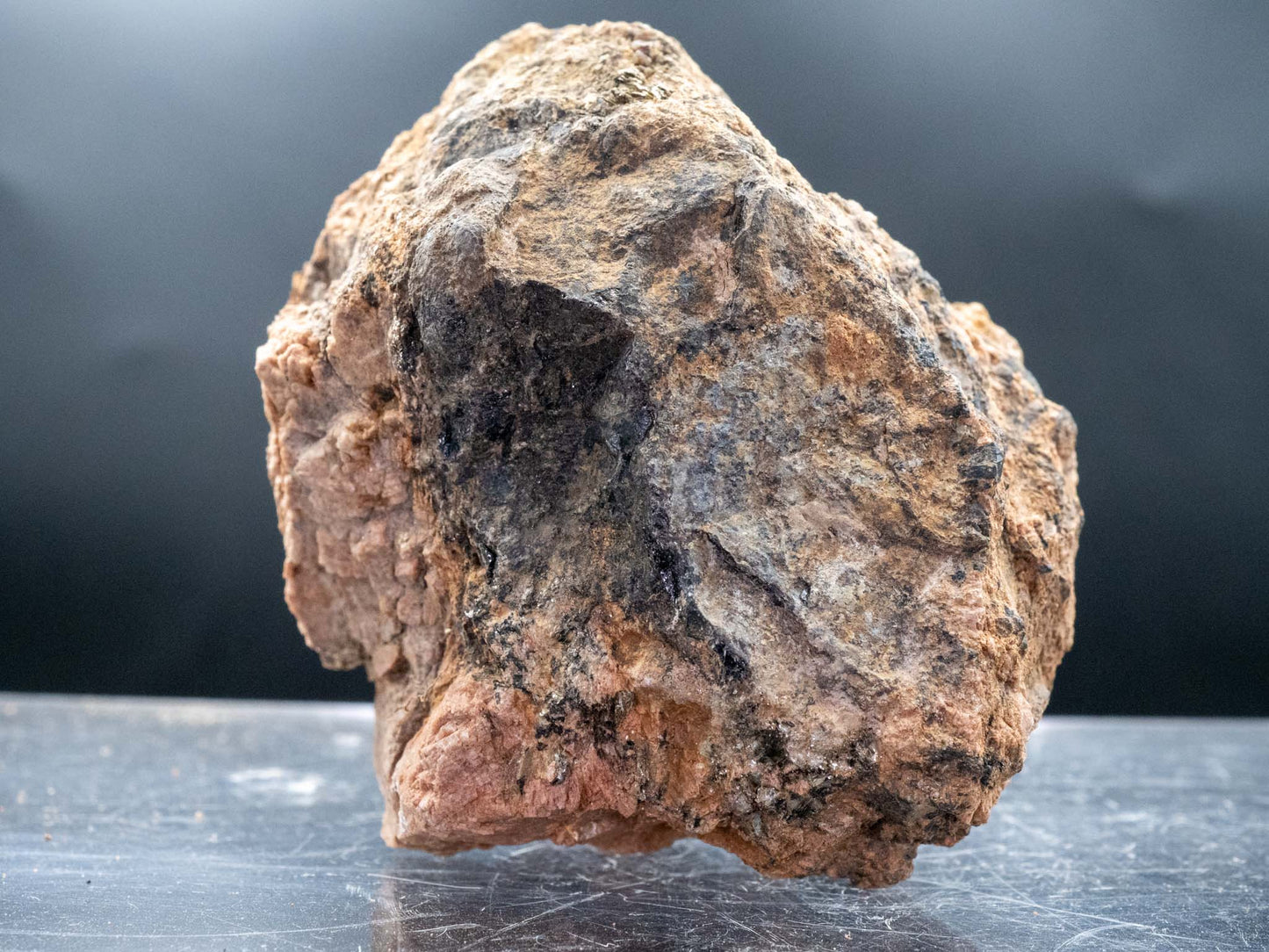
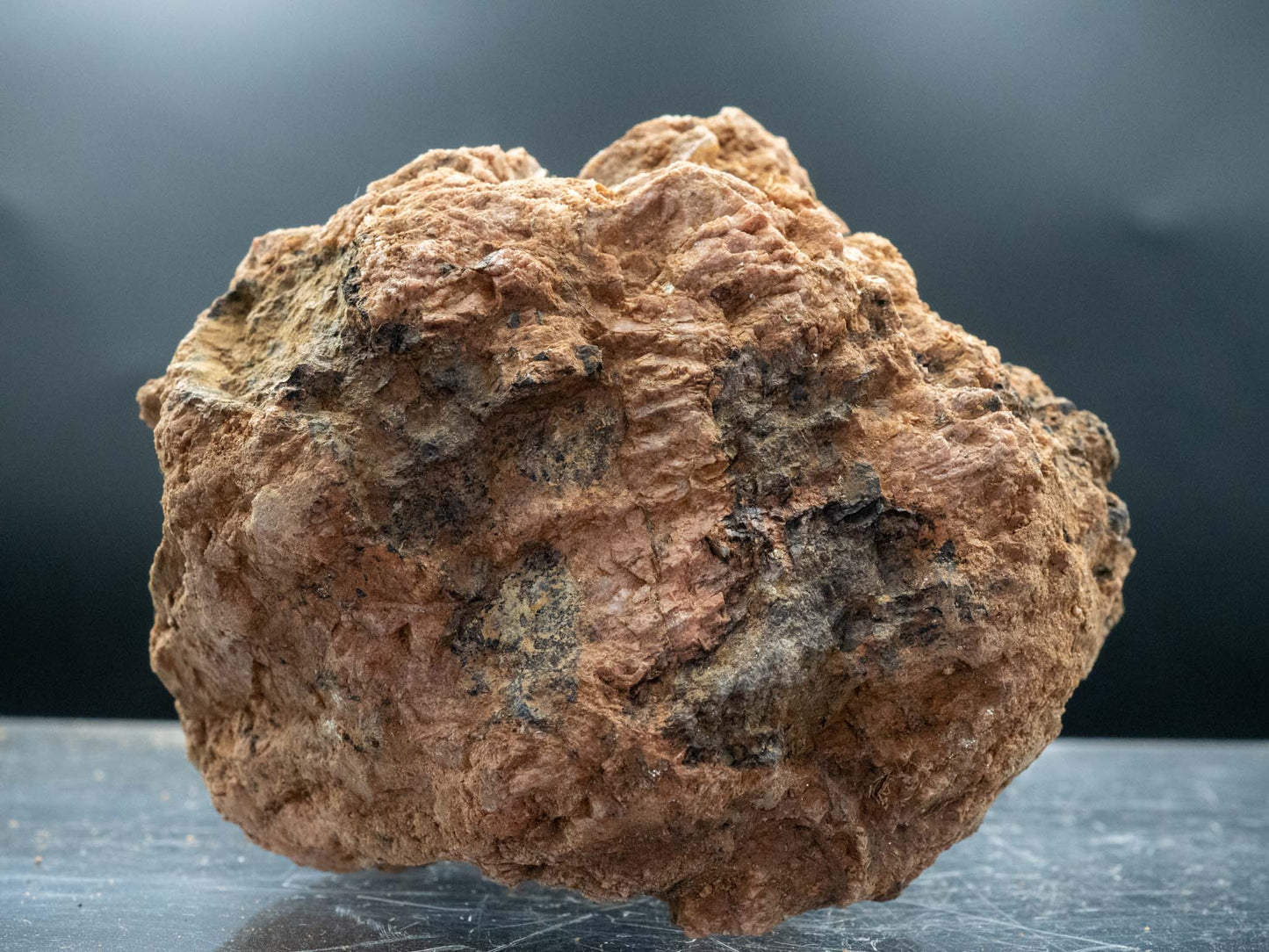
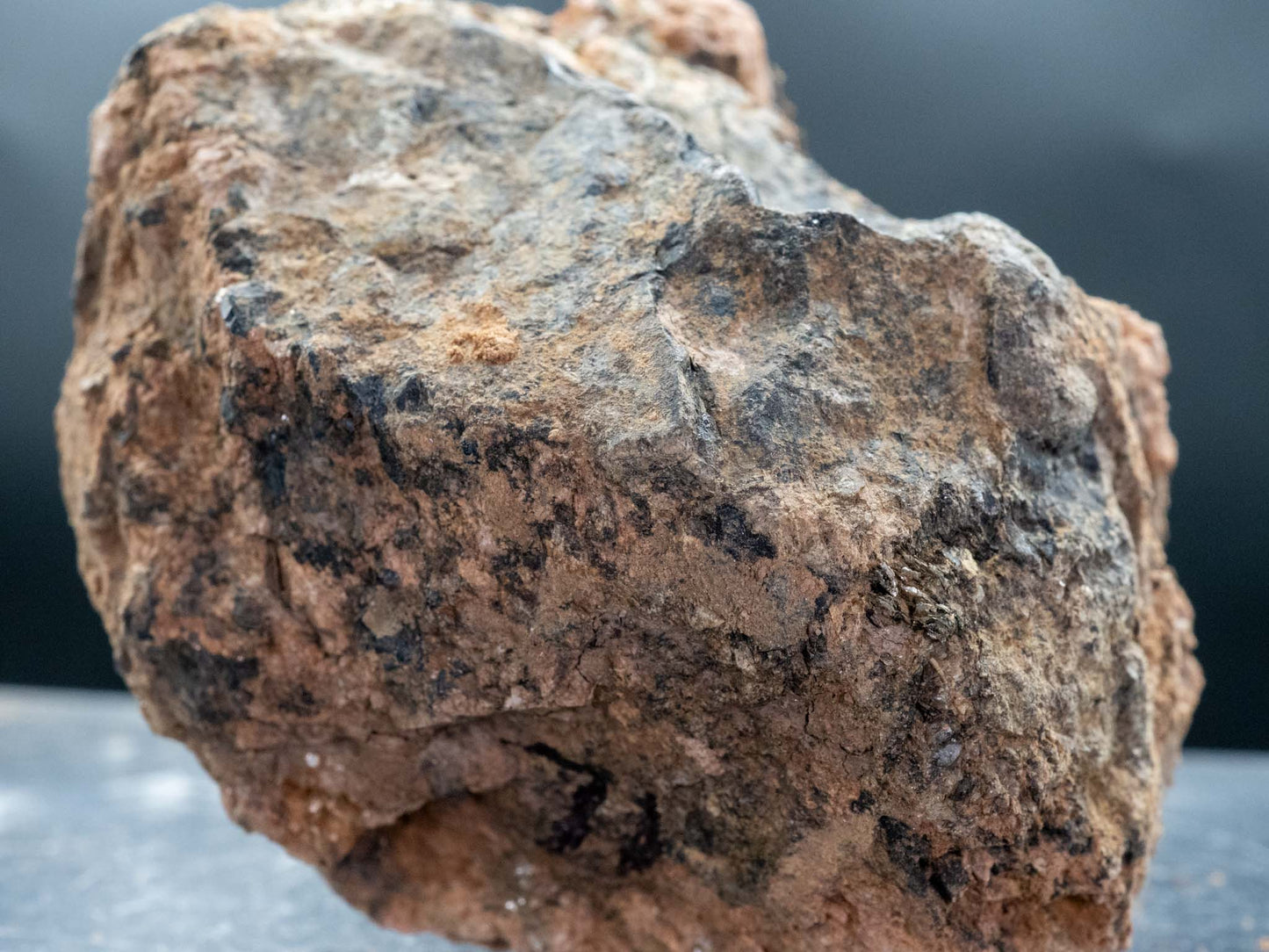
Euxenite-(Y) - Petaca Mining District, Rio Arriba County, New Mexico, USA (Analyzed)
Euxenite-(Y) - Petaca Mining District, Rio Arriba County, New Mexico, USA (Analyzed)
Couldn't load pickup availability
 (Y,Ca,Ce,U,Th)(Nb,Ta,Ti)2O6
(Y,Ca,Ce,U,Th)(Nb,Ta,Ti)2O6
Euxenite-(Y) in the Petaca Mining District
The Petaca Mining District, located in Rio Arriba County, New Mexico, is notable for its rare-earth mineral deposits, including the occurrence of Euxenite-(Y). Euxenite-(Y) is a complex oxide mineral that commonly contains rare earth elements (REEs) along with niobium (Nb) and tantalum (Ta). Here's an overview of its significance in the context of the Petaca Mining District:
Geological Context of the Petaca Mining District
- Location: This district is situated in the northern part of the Picuris Mountains, within Precambrian rock formations.
- Host Rocks: The euxenite-(Y) is typically found in pegmatites, which are coarse-grained igneous rocks rich in rare elements.
- Associated Minerals: Pegmatites in the district host a variety of REE-rich minerals, including allanite, monazite, samarskite, and euxenite-(Y).
Characteristics of Euxenite-(Y)
-
Chemical Composition:
- General Formula: (Y,Ca,Ce,U,Th)(Nb,Ta,Ti)2O6
- The mineral contains yttrium (Y), niobium (Nb), and tantalum (Ta) as its primary components. Uranium (U) and thorium (Th) may also be present, contributing to its slight radioactivity.
-
Physical Properties:
- Color: Brown to black, often with a metallic luster.
- Hardness: 5.5–6.5 on the Mohs scale.
- Luster: Submetallic to vitreous.
- Habit: Typically found in granular masses or as anhedral crystals.
-
Formation Environment:
- Euxenite-(Y) forms during the late stages of crystallization in pegmatitic environments, where rare elements become concentrated.
Mining and Exploration in the Petaca Mining District
-
Historical Mining Activities:
- Mining in the district began in the late 19th century, primarily focused on mica, feldspar, and later, rare-earth elements.
- Euxenite-(Y) has been identified but was not the primary focus of historical mining efforts due to its complex extraction and refinement processes.
-
Current Interest:
- The strategic importance of rare-earth elements has renewed interest in the district for materials like euxenite-(Y) that are sources of yttrium and other critical elements.
Significance of Euxenite-(Y)
-
Yttrium Extraction:
- Yttrium is used in applications such as phosphors in lighting, laser technology, and ceramics.
-
Niobium and Tantalum:
- Essential for the electronics industry due to their use in capacitors and high-strength alloys.
-
Research and Collection:
- Euxenite-(Y) is also valued by mineralogists and collectors for its rarity and complexity.
Challenges
- Radioactivity: Due to its uranium and thorium content, handling and processing euxenite-(Y) require strict safety protocols.
- Economic Viability: The complexity of extracting multiple elements from the mineral poses a challenge for large-scale commercial exploitation.
The Petaca Mining District remains a fascinating area for geologists and collectors alike, with its unique assemblage of rare-earth-bearing minerals like euxenite-(Y). The district highlights the interplay between geology, mineralogy, and the strategic need for rare elements in modern technologies.
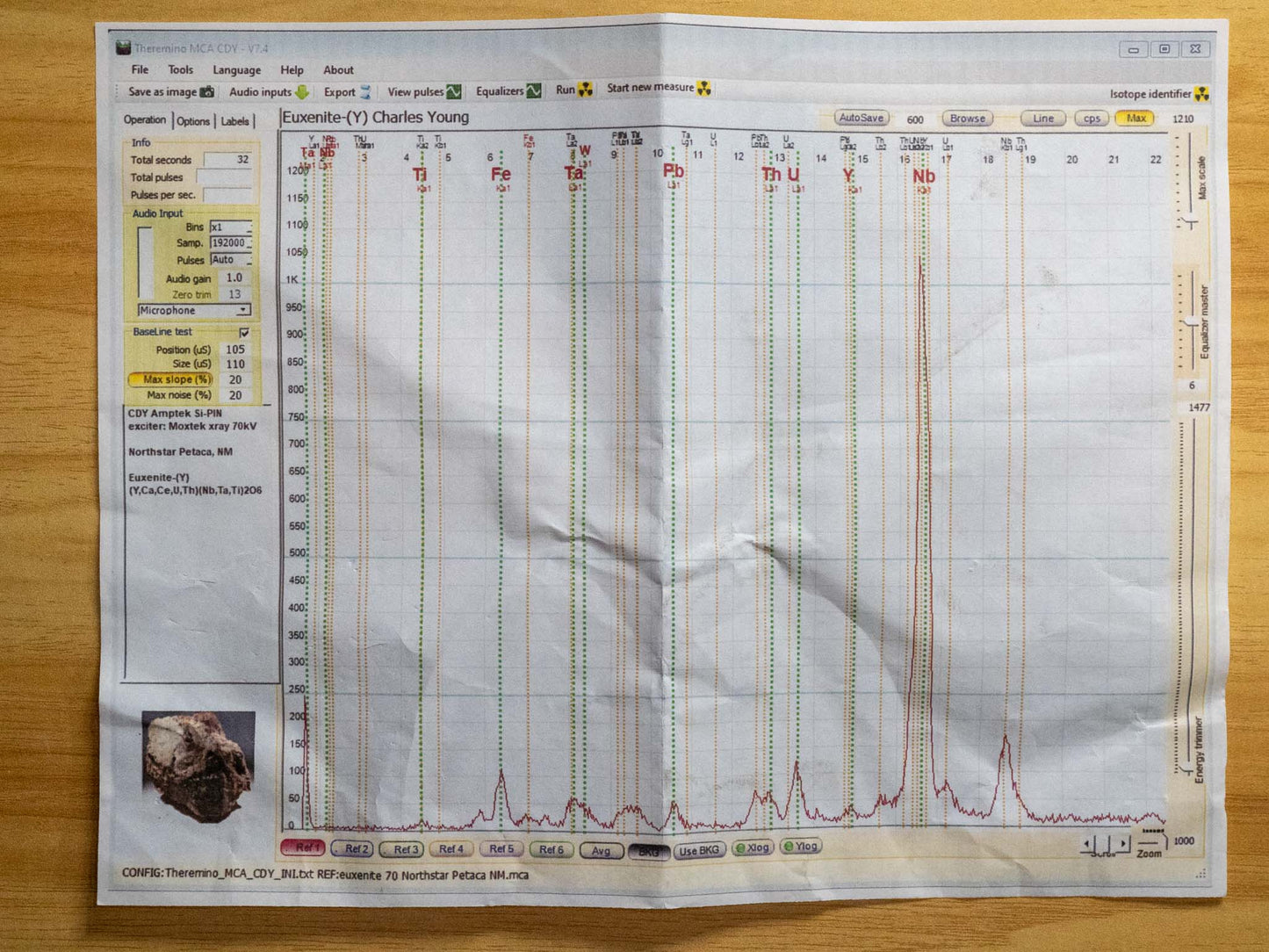
This specimen has been collected and analyzed by Charles Young, and includes a copy of the XRF report.
Approx. specimen size: 75mm x 70mm x 50mm
Approx. specimen activity: 81000 cpm